- Length of Z axis (% of image height)
This parameter defines the depth of the object to be displayed (from top-most to lowest frame of your stack). To avoid calculations in Ám or pixels, the value is given as percent of the Y-axis (i.e. image height). Higher values give more depth to the object and vice versa.
- Enlarge pixels
Enlarges pixels in order to prevent the occurrence of fissures in 3D-images. The latter arise as the surface area of 3-D images is larger than that of the (flat) stacked image. The value has to be increased for objects with high depth.
- Perspective (%)
A value > 0 has the effect that close parts of the displayed object are enlarged compared to those in the background. This is not normally necessary for a 3-D impression. Too high values will distort the object.
- Projection based on depth map
Standard setting, uses (together with the stacked image) the depth map for the generation of spatial and 3-D projections.
- Hologram stacking
Allows for displaying structures of multilayered objects that are hidden when depth-map based is performed. One has to set a rotation angle, filter size an minimum contrast prior to analysing the stack again.
- Back
Closes the 3-D view window.
- Go
Starts the generation of rotations and 3-D images.
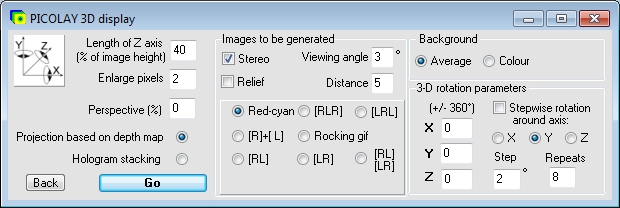
Images to be generated
- 3-D view
For stereoscopic viewing two images (for the left and right eye) are required. However, one can also rotate an object without 3-D.
- Viewing angle
Describes the viewing angle between your eyes when you look at your monitor or at a big screen. For short observation distances use large value (3 - 4░), for long distances (> 3 m Abstand) small values (e.g., 2░).
- Red-cyan
Generates an anaglyph image for red-cyan goggles, left eye red, right eye cyan.
- [RLR] or [LRL] = Right-Left-Right or Left-Right-Left
Generates a 3-D image, with the object shown three times for the right and left eye in alternating order. The result can be received by both, parallel- and cross-viewing, and gives both a convex and concave impression.
- [R] + [L]
Produces to separate images for the left and right eye. These can be used for the generation of MPO files and other purposes.
- Rocking gif
Generates an animated gif image, showing the left- and right-eye image flickering with the frequency set under Options (main window). A rocking gif provides a spatial impression to obervers who can not perform parallel- and cross-viewing.
- [RL] + [LR]
Generates various steroscopic images for different purposes, for cross- [RL] or parallel viewing [LR], side by side or one on top of the other [--], interlaced or as jps file.
-
[RL]
[LR]
Gerates a 3-D images composed of an [RL]- and an [LR]-images one on top of the other. The result can be received by both, parallel- and cross-viewing, and gives both a convex and concave impression.
Background
- Average
Uses the average of all images as background for low-contrast areas. To be used for small rotatin angles.
- Colour
Uses a selected colour as background for low-contrast areas. To be used for large rotation angles. To select the colour RIGHT-click into the image window (pipette function).
3-D rotation parameters
- X, Y and Z
Gives the projection angle of the three axes in the range of 0.0 - 360.0░.
- Stepwise rotation around axis:
Select the axis for stepwise rotation.
- Step
Defines the degree of rotatiopn per step, allow values < 1░.
- Repeats
Gives the number of rotation steps.
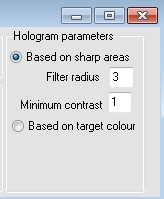
Hologram parameters
- Based on sharp areas
Makes visible all structures that reach the adjusted minimum contrast.
- Filter radius
Defines the size of the search mask for structures.
- Minimum contrast
Defines the contrast threshold at which structures will be visualised. A too small step will display unsharp areas hiding underlying structures. Large values will make low-contrast structures invisible.
- Based on target colour
Generates a hologram based on the intensity of a selected colour (mayvbe a fluorescence dye etc.) not regarding contrast. To select the colour perform a RIGHT-click into the original image as described above.
|